আপুনি যদি অসম চৰকাৰৰ দ্বাৰা পৰিচালিত চৰকাৰী বিদ্যালয়ত ষষ্ট মান শ্ৰেণীত পঢ়ি আছে আৰু আজি আপুনি ইয়াত Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Question Answer in English বিচাৰি আহিছে, তেন্তে চিন্তাৰ কোনো কাৰণ নাই।
আমি আপোনালোকৰ বাবে Assamese Medium নামৰ এই শিক্ষামূলক ৱেবছাইটত SCERT Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Question Answer in English লৈ আহিছোঁ। আপুনি সম্পূৰ্ণ পাঠ্যপুথিৰ প্ৰশ্ন উত্তৰ ইয়াতে পাব।
- You Can Also Read:

Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Question Answer in English 2023
অসমৰ চৰকাৰী বিদ্যালয় ষষ্ট মান শ্ৰেণীৰ বিজ্ঞান বিষয়ৰ চতুৰ্থ অধ্যায় (Shorting Materials Into Group Question Answer) তথা Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Question Answer in English ত আমি Textual Question Answer দিয়াৰ লগতে আমি আপোনালোকৰ বাবে কিছু গুৰুত্বপূৰ্ণ অতিৰিক্ত প্ৰশ্ন উত্তৰ দিবলৈ প্ৰয়াস কৰিছো।
আশা কৰোঁ আপোনালোকে এই লিখনিৰ জৰিয়তে বহু প্ৰকাৰে উপকাৰী হব। তেন্তে আহক কোনো সময় নষ্ট নকৰাকৈ আজি আমি Shorting Materials Into Group Question Answer তথা Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Question Answer in English আলোচনা কৰোঁ।
Textbook Question Answer
Class 6 Science Chapter 4 Question Answer in English ত আমি প্ৰথমতে আলোচনা কৰিব গৈ আছো Exercise ত দিয়া প্ৰশ্নবোৰৰ উত্তৰ।
Q. 1. Name five objects which can be made from wood.
Ans. Table, Chair, Doors, Boat, and Bed.
Q.2. Select those objects from the following that shine: Glass bowl, plastic toy, steel spoon, cotton shirt
Ans. Glass bowls and steel spoons are shining objects.
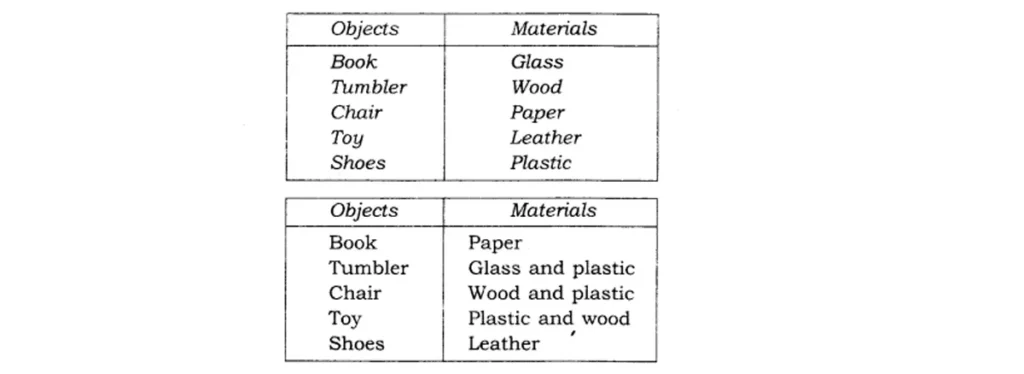
Q.3. Match the objects given below with the materials from which they could be made. Remember, an object could be made from more than one material and a given material could be used for making many objects.
Ans:
Q. 4. State whether the statements given below are ‘true’ or ‘false’.
(i) Stone is transparent, while glass is opaque.
Ans. False
(ii) A notebook has luster while an eraser does not
Ans. False
(iii) Chalk dissolves in water.
Ans. False
(iv) A piece of wood floats on water.
Ans. True
(v) Sugar does not dissolve in water.
Ans. False
(vi) Oil mixes with water.
Ans. False
(vii) Sand settles down in the water.
Ans. True
(viii) Vinegar dissolves in water.
Ans. True
Q. 5. Given below are the names of some objects and materials: Water, basketball, orange, sugar, globe, apple, and earthen pitcher Group them as:
(a) Round-shaped and other shapes
Ans. (i) Round shaped: Basketball, apple, orange, globe, earthen pitcher.
(ii) Other shapes: Water, sugar.
(b) Eatables and non-eatables
Ans. (i) Eatables: Water, orange, sugar and apple.
(ii) Non-eatables: Basketball, globe, and earthen pitcher.
Q. 6. List all the items known to you that float on water. Check and see if they will float on an oil or kerosene.
Ans. (A) List of some items that float on water: Paper, Wood, Thin plastic sheets, Wax, Ice, thermocol, and Oil.
(B) List of items that float on oil: Paper, Plastic sheet, Wax, Thermocol, Wood
(C) List of items that float on kerosene: Paper, thermocol, thin plastic sheet.
Q. 7. Find the odd one out from the following:
(a) Chair, Bed, Table, Baby, Cupboard
Ans. Baby (all others are non-living)
(b) Rose, Jasmine, Boat, Marigold, Lotus
Ans. Boat (all others are flowers)
(c) Aluminium, Iron, Copper, Silver, Sand
Ans. Sand (all others are metals)
(d) Sugar, Salt, Sand, Copper sulfate
Ans. Sand (all others are soluble in water)
Additional Question Answer
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Question Answer ত আমি যি Additional Question Answer দিবলৈ চেষ্টা কৰিছোঁ সেই সকলোবোৰৰ ভিতৰত আছে কিছু গুৰুত্বপূৰ্ণ অতি চমু প্ৰশ্ন উত্তৰ, কিছু চমু প্ৰশ্ন উত্তৰ আৰু কেইটামান দীঘল প্ৰশ্ন উত্তৰ। তেন্তে আহক আমি আলোচনা আৰম্ভ কৰোঁ।
Very Short Type Question Answer
1. Why do we need to group materials? Give one reason.
Ans: We often group materials for our convenience. It helps to describe their properties.
2. Suggest two bases on which we can group objects.
Ans:
- Material used in making the object, e.g. wood or metal/plastic.
- The material of the object is soft or hard, or the substance is soluble or insoluble in water.
3. Is a substance that can be compressed soft or hard?
Ans: Soft.
4. Select a lustrous material out of the following substances:
Ans: Aluminium.
5. Which material is generally used for making pens? Wood, aluminum, plastic, cotton
Ans: Plastic or metal.
6. Is oil soluble in water?
Ans: Oil does not dissolve in water so it is insoluble in water but floats on the surface of water.
7. Name two objects which are made from opaque materials.
Ans: Wooden doors, blackboard/steel plate.
8. What is common between salt and sand?
Ans: Both have mass and are in a solid state.
9. List three liquids that are transparent.
Ans. Water, alcohol, and Acetone/Benzene.
10. Write two substances that are made from leather.
Ans: Belt and shoes.
11. Name some substances which are made from plastics.
Ans: Toys, plates, cups, buckets, baskets.
12. Which is more hard, sponge or iron?
Ans: Iron is harder than sponge.
13. Write two gases that are soluble in water.
Ans: Oxygen, Carbon dioxide.
14. Name two gases which are insoluble in water.
Ans: Hydrogen and Nitrogen.
Important Short Type Question Answer
1. Write any four properties of materials.
Ans:
- Appearance
- Hardness
- Solubility
- Float or sink in water
- Transparency
2. Why is a tumbler not made with a piece of cloth?
Ans: We use tumblers made of glass, plastic, and metal to keep liquid. These substances can hold a liquid. A tumbler made of cloth cannot hold a liquid because:
(i) The cloth piece is not hard enough to hold liquids and
(ii) Cloth piece has very minute pores through which the liquid oozes out.
3. What are the similarities between iron, copper, and aluminum?
Ans:
- They all have lustre,
- They are all metals,
- They are hard.
4. Mention some materials which are made up of paper.
Ans: Books, notebooks, newspapers, toys, calendars, etc.
5. Why is water important for our body?
Ans: Water can dissolve a large number of substances, so it is needed by the body. It is also a major part of our body cells.
6. What is the basis for sorting materials?
Ans: Materials are grouped on the basis of similarities or dissimilarities in their properties.
7. What is the reason for grouping materials?
Ans: Materials are grouped for our convenience to study their properties and also observe any patterns in these properties.
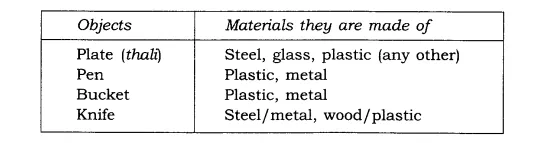
8. Make a table of objects and materials they are made of:
Ans:
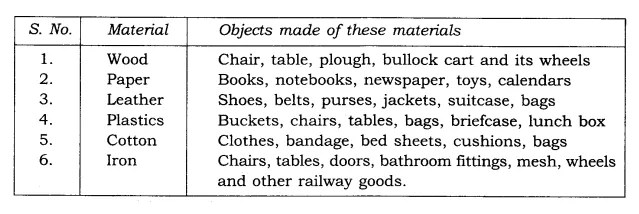
9. Make a table of different types of objects that are made from the same material.
Ans:
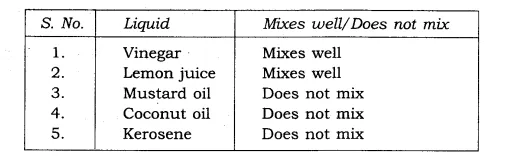
10. Make a table and find out whether the following materials mix with water: Vinegar, Lemon juice, Mustard oil, Coconut oil, and Kerosene.
Ans:
11. Metals have lustre (shine). Give a reason why some metal articles become dull and lose their shine.
Ans: Metals when exposed to air react with moisture and gases present in it, thereby forming a dull layer of some other compound on it.
12. Kerosene, coconut oil, and mustard oil do not dissolve in water, even on shaking. They separate after some time forming two different layers. Explain why.
Ans: The molecules of water do not intermingle (mix) with the molecules of oil. The space between the molecules of water is not taken by oil, so they are immiscible in water.
13. Name a non-metal that has lustre.
Ans: Iodine.
14. Metals generally occur in a solid state and are hard. Name a metal that exists in a liquid state and a metal that is soft and can be cut with a knife.
Ans: Mercury is a metal that exists in a liquid state. Sodium and Potassium are soft metals and can be cut with a knife.
15. Name the naturally occurring hardest substance known.
Ans: Diamond, is made up of carbon (non-metal).
16. Why is water called a universal solvent?
Ans: Water dissolves a large number of substances in it. So it is called a universal solvent.
Important Long Question Answer
1. ‘Grouping of objects helps the shopkeeper.’ Justify the statement.
Ans: Proper grouping of objects helps shopkeepers in the following ways:
(i) He can locate the required object easily and quickly.
(ii) He can easily come to know what stocks are going to finish and he should purchase them for his customers.
2. Describe an experiment to prove that water is transparent.
Ans: Take a beaker half-filled with clean water. Put a coin in a beaker of water.
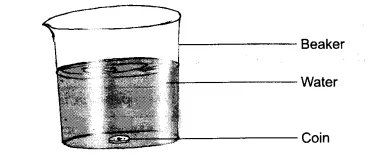
Place the beaker undisturbed for a few minutes where enough light is present. Now, observe the coin immersed in water from the top of the beaker. Are you able to see the coin? You can clearly see the coin immersed in water. This proves that water is a transparent liquid.
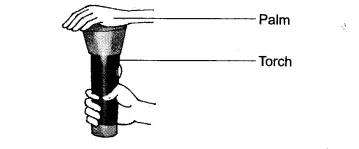
3. Write an experiment to show that our palm is translucent.
Ans: Cover the glass of a torch with your palm in a dark place. Switch on the torch and observe from the other side of the palm. We see that the light of the torch passes through the palm but not clearly. This experiment shows that our palm becomes translucent when a strong beam of light passes through it.